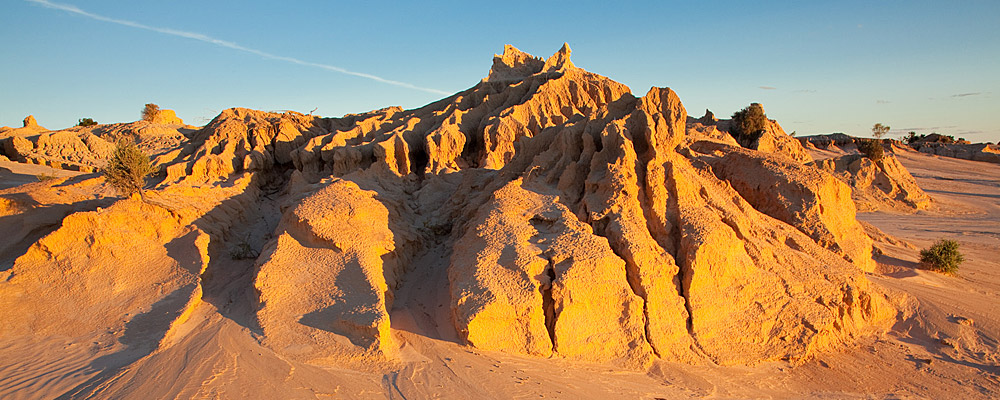
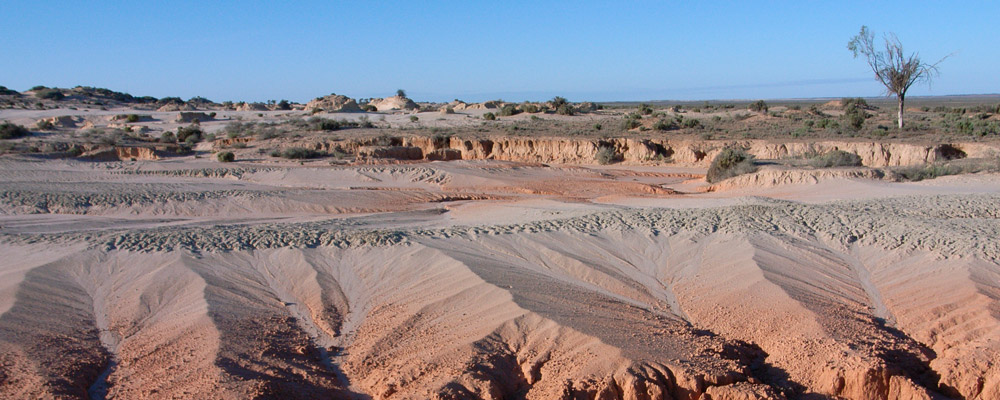
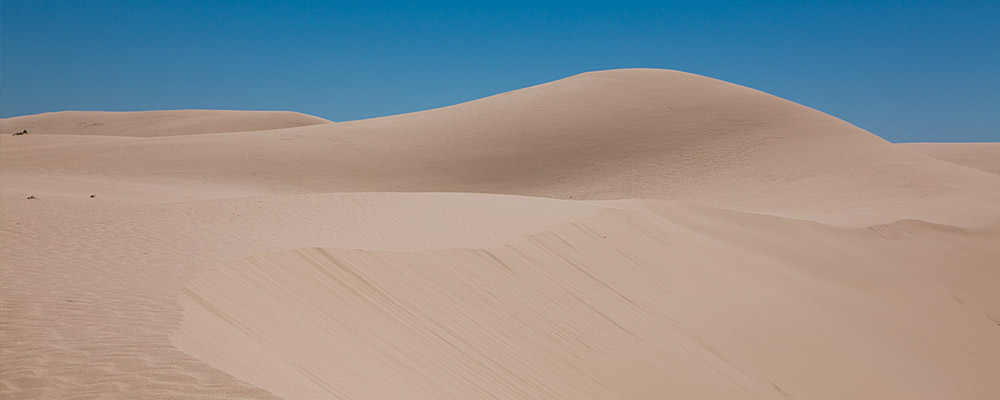
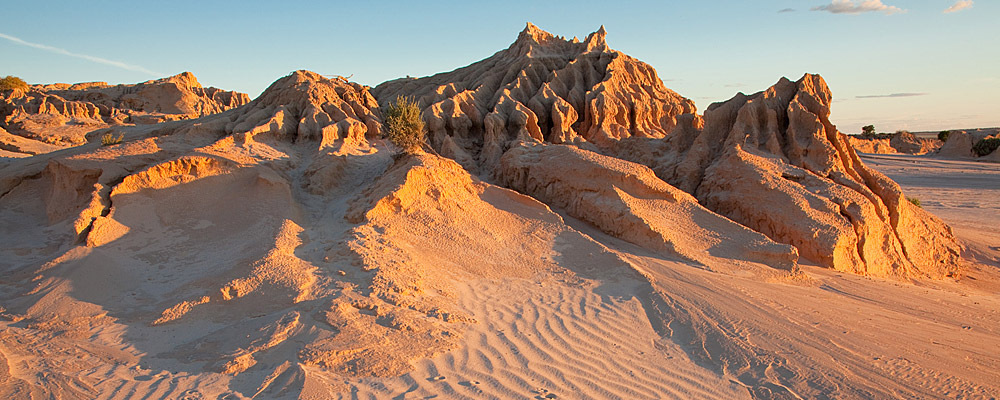
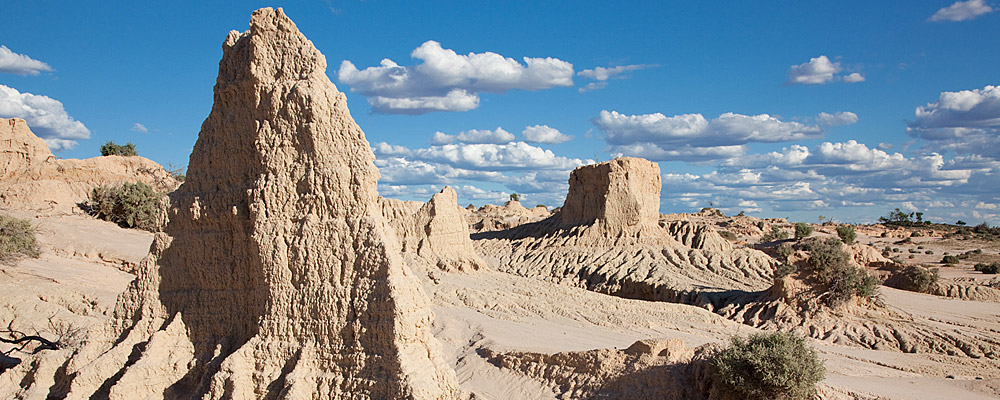
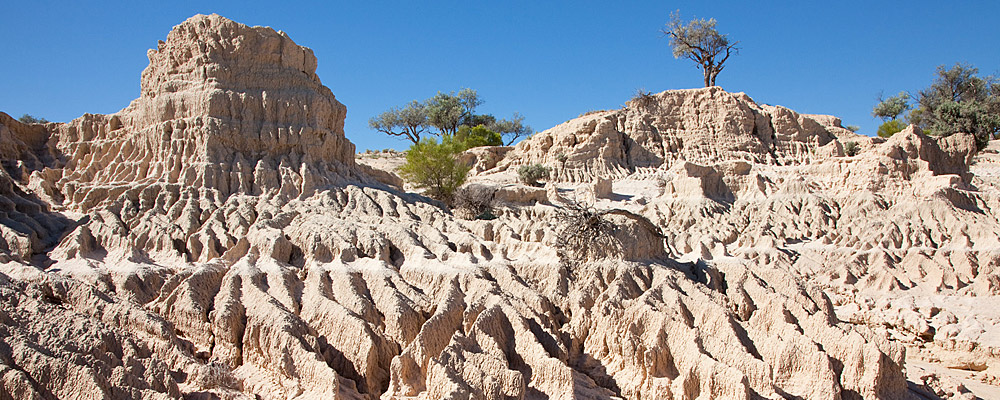
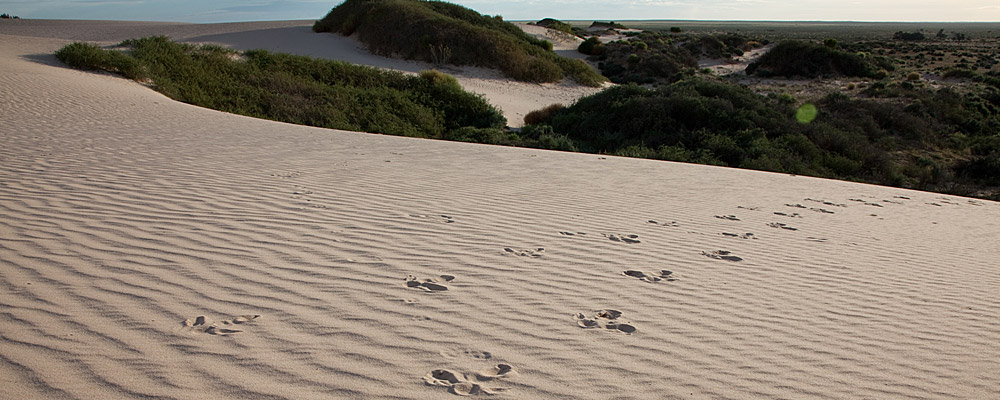
Understand Mungo
World Heritage
Detailed World Heritage criteria for Willandra Lakes Region
Outstanding example representing a major stage of the Earth's evolutionary history.
The Willandra Lakes Region represents major stages of the Earth's geological history, particularly associated with the response to major glacial-interglacial fluctuations. The World Heritage values include:
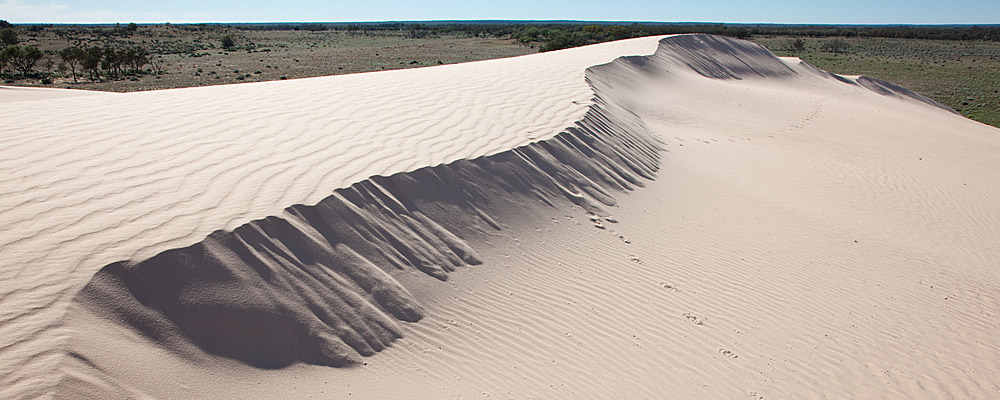
non-glaciated, low-latitude lacustrine landscape lake basins which include:
- 0
- lunettes;
- 1
- inter-lake areas between major lake basins;
- 2
- connecting channels adjacent to the lake system;
- 3
- connecting dunefields adjacent to the lake system;
- 4
- unusually large clay dunes; and
- 5
-
complex downstream variability in the character of the lacustrine system;
fossil dunes and lake sediments including those which show: - 6
- evidence of Pleistocene climatic changes and landscape history for the geomorphological record spanning well over 100,000 years;
- 7
- detailed stratigraphic, geochemical and pedological evidence for climatic and related environmental changes;
- 8
- how non-glaciated inland regions were affected by the major climatic fluctuations associated with oscillations in ice sheets;
- 9
- the influence of the westerly winds that prevailed throughout the period of dune formation, a period extending from at least 100,000 years to about 15,000 years ago; and
- 10
-
evidence of giant extinct marsupial species.
extensive flat plains of lake floors and sedimentary carbonates which show: - 11
- evidence of past salinity fluctuations and the stability of the landscape in this region; and
- 12
-
evidence of the area's response to major climate change.
stunted blue bush (Maireana sedifolia, M. pyramidata) and saltbush (Atriplex stipulata) on the lake floor showing evidence of final saline phases of lakes.
Unique cultural tradition.
The Willandra Lakes Region demonstrates an exceptional sequence of Aboriginal cultural occupation extending over tens of thousands of years, including an outstanding record of human responses to major changes over time in climate and environments (e.g. due to increasing aridity). The World Heritage values include:
landforms and locations which greatly extend our understanding of Australia's environmental and Aboriginal cultural history, including:
- exposures of sedimentary sequences which reveal Pleistocene sedimentary profiles and associated archaeological and palaeontological materials;
- extensive intact lakeshore landforms that may contain extensive archaeological and palaeontological materials; and
- the remains of hearths, including those with considerable antiquity, which have provided an ideal source for palaeomagnetic measurements;
- archaeological sites which occur within stratified sedimentary sequences and provide evidence for the antiquity and continuing presence of human occupation;
- archaeological sites which contain evidence of utilisation of lacustrine resources during lake full phases, and rangeland resources during arid phases;
- archaeological sites which demonstrate continuity of human occupation for the region through fluctuations in lake levels drying of the system about 15,000 years ago through the Holocene period and up to historic times;
- archaeological sites which provide outstanding examples of hunting and gathering, a way of life that has dominated the Australian continent up to modern times, including:
- evidence of human occupation of, and interaction with, the landscape of lakes, lunettes and sand dunes over time in the form of campsites, middens, fireplaces, quarries, knapping floors and burials; and
- campsites and fireplaces that reflect people's hunting, gathering and fishing diet;
- burial sites which are of global significance for the antiquity of burial practices represented and also for the information they provide on the development of human societies, including Pleistocene and Holocene burial sites; and
- burial sites with associated mortuary goods and evidence of ritual burials that demonstrate the antiquity of particular burial practices and the development of religious beliefs and systems over time.